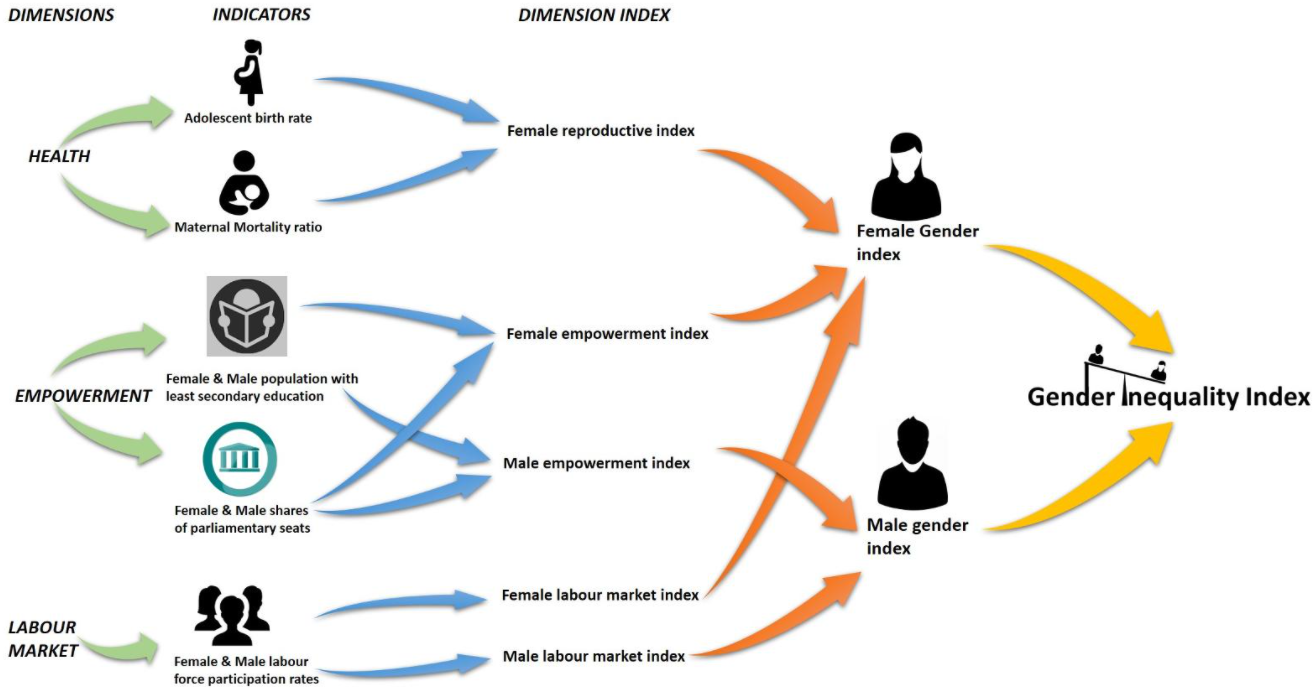
TECHNICAL NOTE
This GEM platform offers two key functions:
- It visualizes gender inequality at sub-national level, including gender inequality index (GII), and gender gaps in various sectors such as education, health, employment, household decision-making etc. using periodically updated and official gender dis-aggregated data.
- It offers gender data repository for public use.